GitLab is an open source project, but also a commercial project. For historic
reasons, we have two Git repositories: gitlab-ce for GitLab Core and
gitlab-ee for GitLab Enterprise packages (you can read our recent blog post explaining GitLab self-managed tiers).
While we're working on having a single codebase, we still need to regularly
merge gitlab-ce into gitlab-ee since most of the development happens on
GitLab Core, but we also develop features on top of it for GitLab Starter, Premium, and Ultimate.
How we used to merge GitLab CE into GitLab EE
Until December 2017, the merge of gitlab-ce into gitlab-ee was manual
on a daily basis with basically the following commands (see the full documentation):
# the `origin` remote refers to https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-ee.git
# the `ce` remote refers to https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-ce.git
git fetch origin master
git checkout -b ce-to-ee origin/master
git fetch ce master
git merge --no-ff ce/master
At this point, since we'd merge a day's worth of GitLab Core's new commits,
chances were good we'd see conflicts.
Most of the time, the person responsible for this process would handle the
conflict resolutions, commit them and push the ce-to-ee branch to GitLab.com.
There were a few problems with this approach:
- GitLab's development pace is fast, which means the longer we go without a
merge, the more changes there are and thus more opportunities for conflicts - If we had many conflicts, it could take a significant amount of time for the
developer responsible for the merge - The developer performing the merge wasn't always the best person to resolve the
conflicts - Significant time was spent identifying and notifying developers to help resolve conflicts
The solution
Our plan was to have a single script that would automate the merge, and in the
case of conflicts, identify the person best suited to resolve each of them.
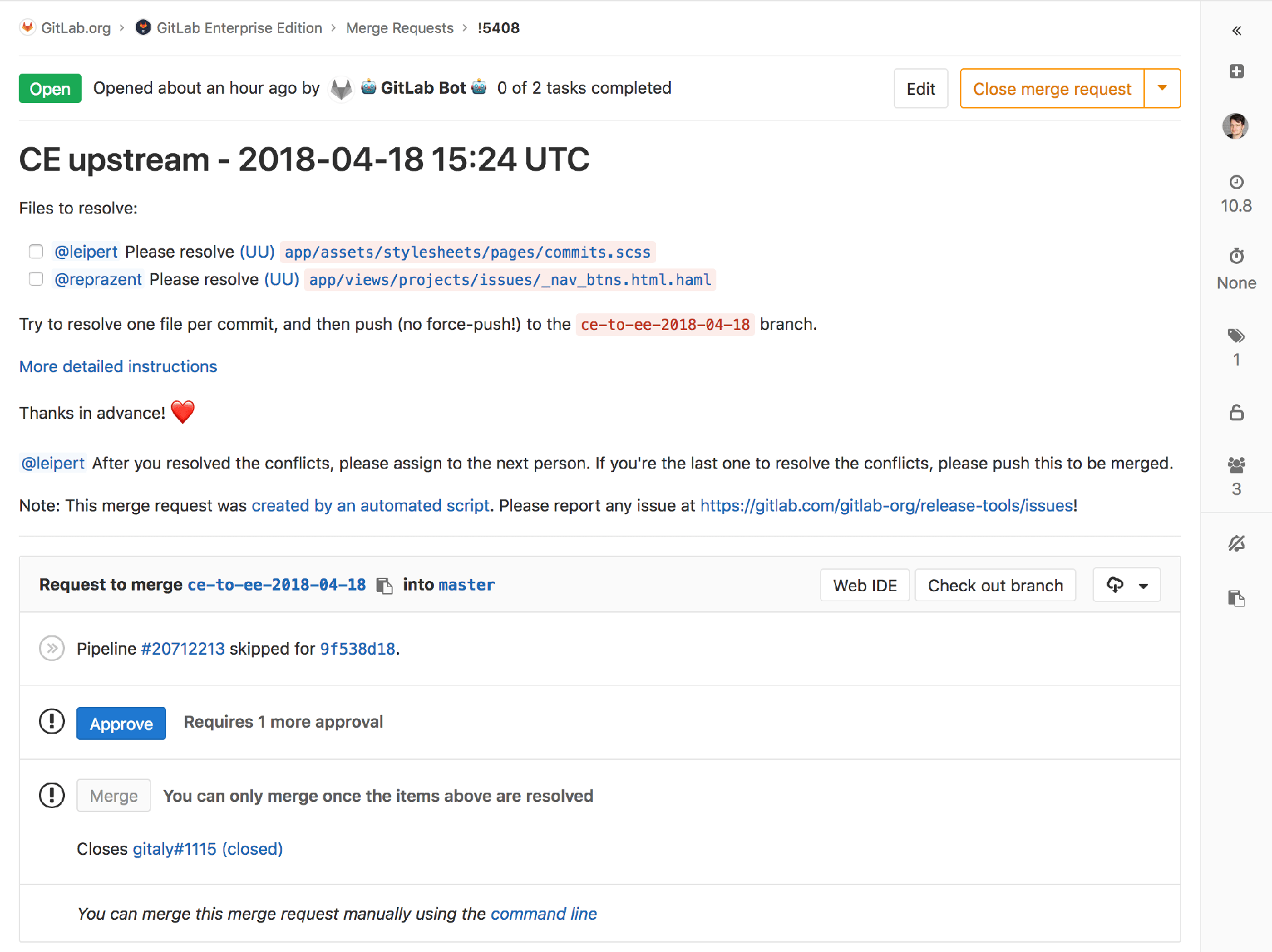
It would then create the merge request using the GitLab API and a
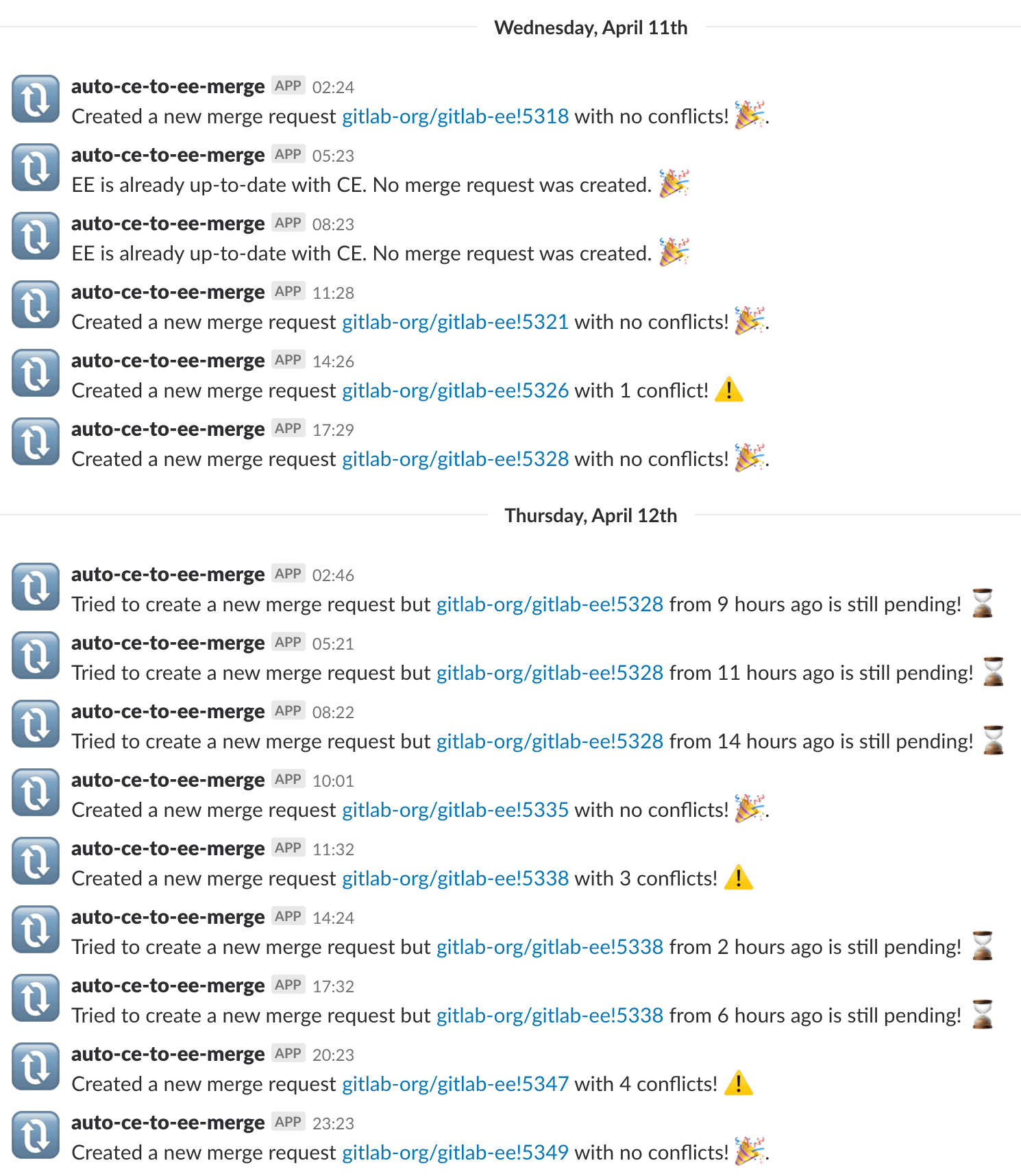
GitLab API Ruby wrapper, and post a message in Slack when a new merge request
was created or an existing one was still pending.
Finally, we'd use GitLab's pipeline schedules to run the script every three hours.
Step 1: Write the script
We chose to write the script in our release-tools project, since it already
had a strong foundation for working with the relevant Git repositories.
This script was written iteratively as a set of classes over the course of a few
months:
- Add the ability to find/create a merge request
- Move remotes to the
Projectclasses and get rid of theRemotesclass - Add
head,status,log,fetch,checkout_new_branch,pull,push, andmergetoRemoteRepository - Introduce a new
CommitAuthorclass
The last piece of the puzzle was the new upstream_merge Rake task.
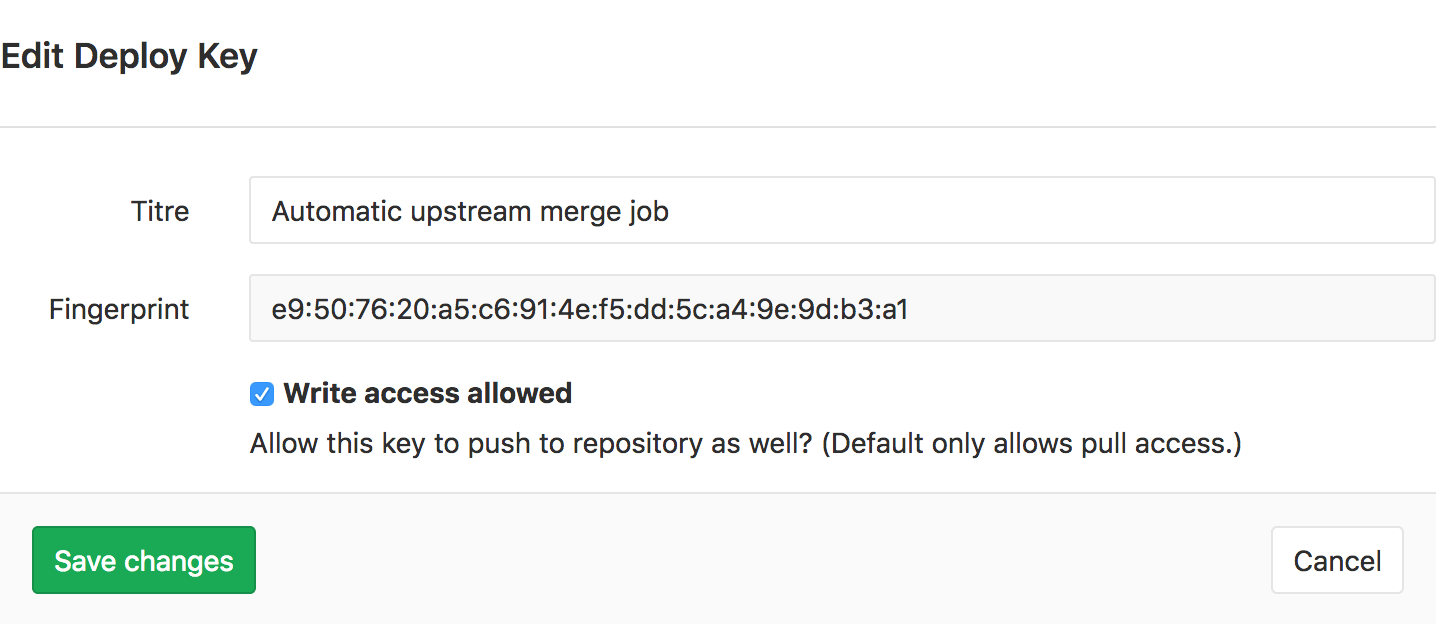
Step 2: Create a pair of SSH keys and add the public key to the gitlab-ee project
Under Repository Settings > Deploy Keys of the gitlab-ee project:
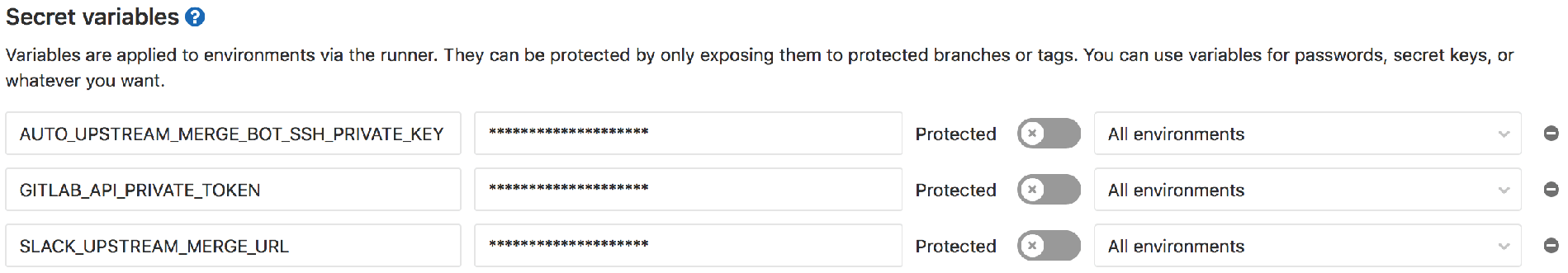
Step 3: Create secret variables in the release-tools project
Under CI / CD Settings of the release-tools project, create three secret
variables:
AUTO_UPSTREAM_MERGE_BOT_SSH_PRIVATE_KEYfor the SSH private keyGITLAB_API_PRIVATE_TOKENis a personal access token for our@gitlab-bot
userSLACK_UPSTREAM_MERGE_URLwhich is the Slack webhook URL we created
specifically for this job and used in ourSlack::UpstreamMergeNotificationclass
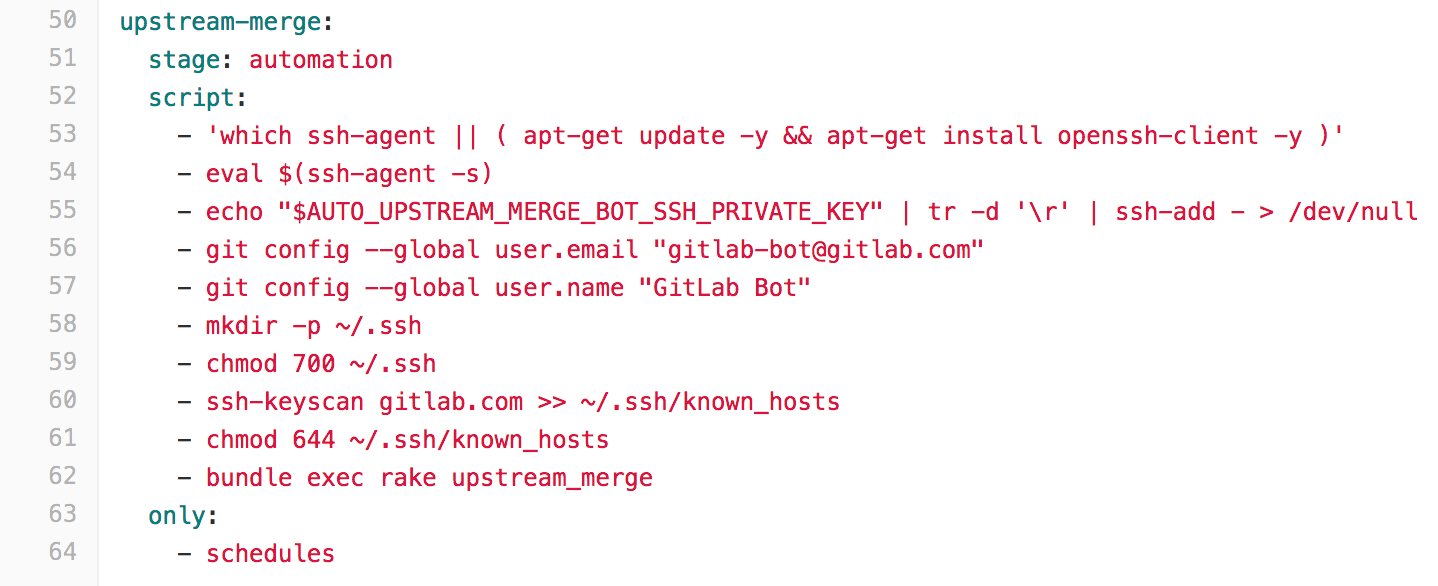
Step 4: Add a new CI job that runs the upstream_merge Rake task for pipeline schedules only
This was heavily inspired by GitBot – automating boring Git operations with CI.
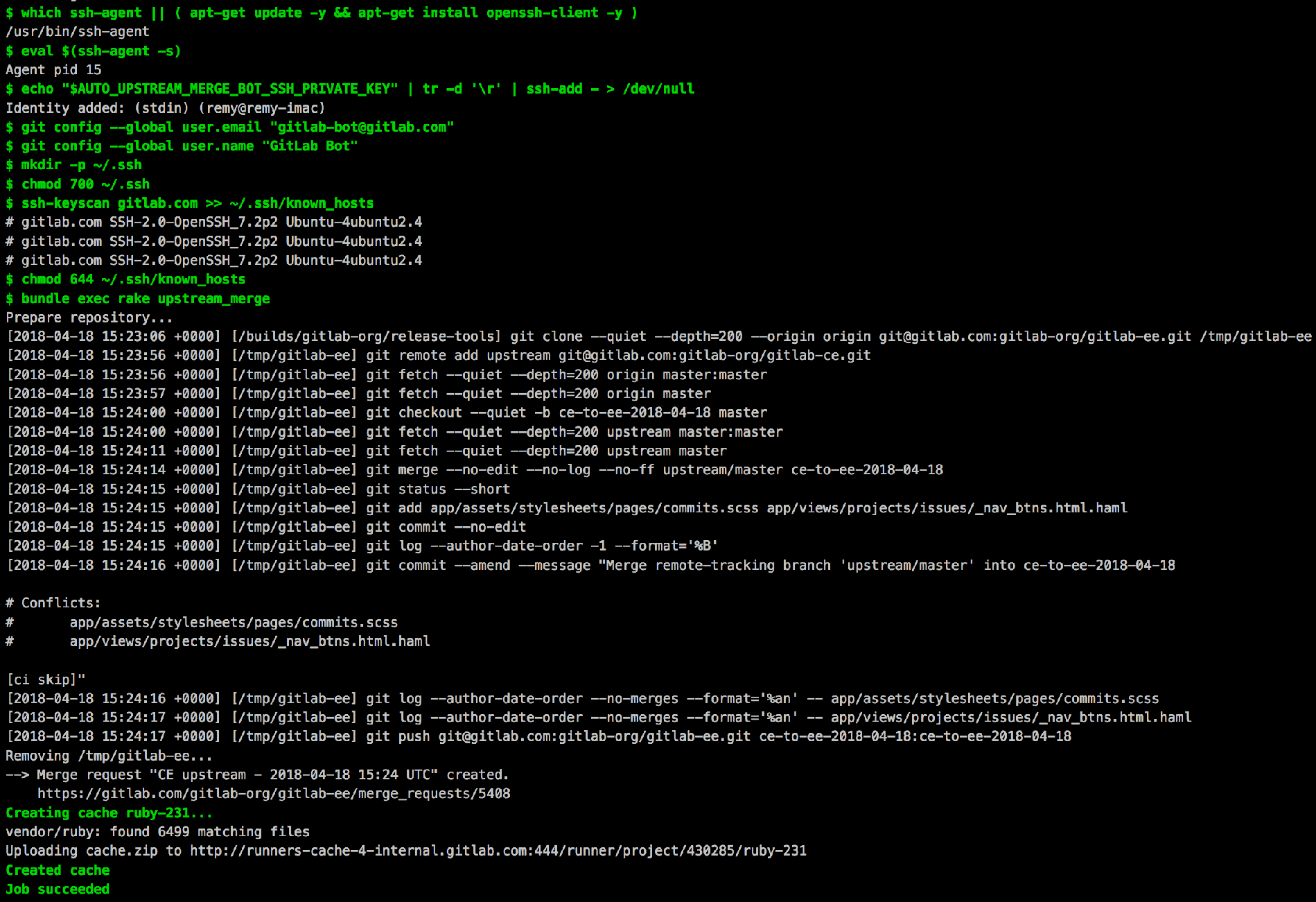
Create a new upstream-merge CI job that:
- Adds the SSH private key to the
~/.sshfolder - Add
gitlab.comto the~/.ssh/known_hostsfile - Runs
bundle exec rake upstream_merge
You can check out the task for yourself.
Step 5: Create a pipeline schedule that runs every three hours
Under Schedules of the release-tools project:
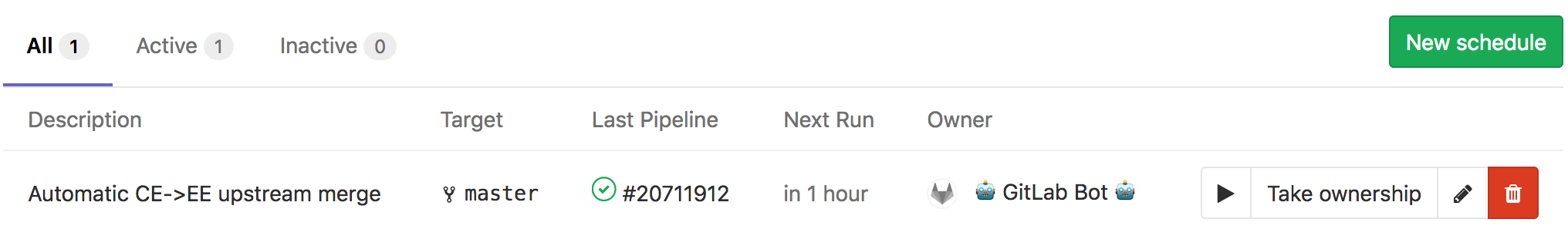
Step 6: Let the bot work for us!
The CI job:
The Slack messages:
The merge request:
What are the benefits?
Since we started automating this process in December 2017, our dear
@gitlab-bot created no fewer than 229 automatic merges, and we started
noticing the benefits immediately:
- Automating the merge request creation saved developers time and removed a manual
chore. - Automatically identifying the developer who introduced a conflict and assigning
them to resolve it spread out the workload and reduced bugs caused by improper
conflict resolution. - Performing the merge automatically every three hours instead of manually once a
day led to fewer changes at a time and a reduced number of conflicts.
The last, perhaps least visible, but most important benefit, is that we reduced
developer frustration and increased happiness by removing a tedious chore.