This blog post was a collaboration between William Arias, from Gitlab, and Vincent D. Warmerdam, from Rasa. You can find the same blog post on Rasa's blog.
Create and Deploy Custom Actions Containers to Rasa X using Gitlab DevOps Platform
Virtual assistants do more than just carry on conversations. They can send emails, make updates to a calendar, or call an API endpoint. Essentially, they can do actions that add significant value and convenience to the user experience.
In assistants built with Rasa*, this type of functionality is executed by custom code called custom actions. As with any code you run in production, you’ll need to think about how you want to deploy updates to custom actions. In this blog post, we’ll show you how to set up GitLab to deploy custom action Docker containers to your Kubernetes cluster. If we follow good DevOps practices we can greatly speed up the development and quality of our virtual assistants.
- Rasa Open Source is a machine learning framework for building text and voice-based virtual assistants. It provides infrastructure for understanding messages, holding conversations, and connecting to many messaging channels and APIs. Rasa X is a toolset that runs on top of Rasa Open Source, extending its capabilities. Rasa X includes key features for sharing the assistant with test users, reviewing and annotating conversation data, and deploying the assistant. Learn more about Rasa.
Deployment high-level overview
The typical workflow for deploying a new version of custom actions is outlined below.
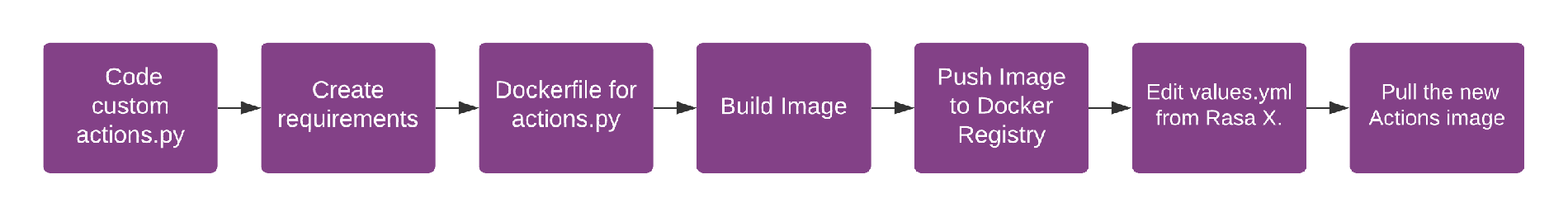
Every change to your custom actions code will require a new container image to be built and pulled by Rasa X. Gitlab CI/CD can save you from doing a lot of manual work and automate steps like the ones described in the workflow above. Let's see how to do it.
Using Rasa with Gitlab DevOps Platform
Let's create a pipeline that will automate manual steps.


