Machine learning can be a powerful tool in software development, but not if it has to live apart from existing engineering workflows. DevSecOps teams, including MLOps, can now integrate OctoML CLI into GitLab’s CI/CD Pipelines to unify workflows and leverage existing deployment and monitoring infrastructure. This integration makes it easier to catch bugs and model performance degradations early in the ML development cycle.
The OctoML Platform is a machine learning model optimization and deployment service powered by octoml.ai. Machine learning has grown in popularity in DevSecOps, along with AI, because of its ability to learn and model how to perform complex tasks as a human would and then automate those tasks.
How does CI/CD apply to machine learning?
Once a machine learning model has been successfully deployed, it can get stale over time and its accuracy could degrade, a situation called “data drift”. Data drift causes newer inferencing data to drift away from the data used to train the model. In the retail industry, this can happen because of seasonality, as an example.
Production models must be regularly refreshed by retraining their weights with the latest data. Applying CI/CD concepts borrowed from software engineering, the OctoML CI integration makes the deployment process for trained/re-trained models automated and repeatable.
How OctoML CLI and GitLab work together
New commits to your inference code repository can run OctoML CLI in your GitLab pipeline to automatically optimize machine learning models for lowest cost per inference and lowest latency, and then deploy the optimized model to your cloud registry. For customers looking for more granular packaging formats that integrate with existing containerization systems, OctoML offers Python wheel packaging and will soon offer YAML configuration files. To reduce model latency and serving costs, OctoML searches through multiple acceleration engines such as Apache TVM, ONNX Runtime, and TensorRT and then suggests the ideal CPU or GPU hardware type on AWS, Azure, or GCP.
Choice in cloud deployment targets
Using OctoML CLI, developers can send any trained model to OctoML’s SaaS platform for cost efficiency and cloud hardware benchmarking. By adapting and optimizing the trained model to leverage hardware intrinsics in CPU and GPUs, OctoML makes inferences run faster in production, thus saving users on cost per inference and improving the user experience of ML applications.
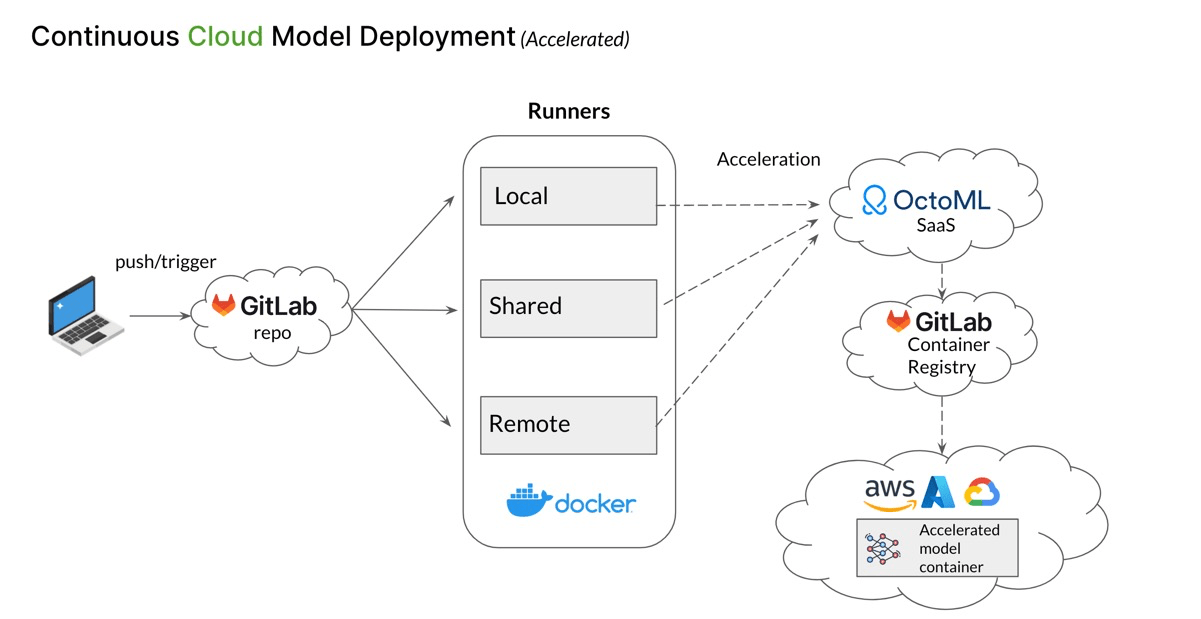
The cloud workflow is designed for enterprise and production deployments. Here’s how it works:
- The initial push from a developer to the GitLab repository launches a local, shared, or remote runner.
- The runner will send the updated, trained model first to OctoML’s platform for acceleration and hardware adaptation.
- Then, the pipeline pushes the accelerated model container to the GitLab Container Registry.
- Finally, it deploys the container to a managed Kubernetes service in any of the major cloud providers.
Models deployed via the accelerated cloud workflow not only provide end users the lowest latency user experience but also save the organization compute costs at inference time, which can amount to [90% of a production machine learning application’s compute costs](https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/machine-learning/reduce-ml-inference-costs-on-amazon-sagemaker-with-hardware-and-software-acceleration/).
Four required stages for every pipeline
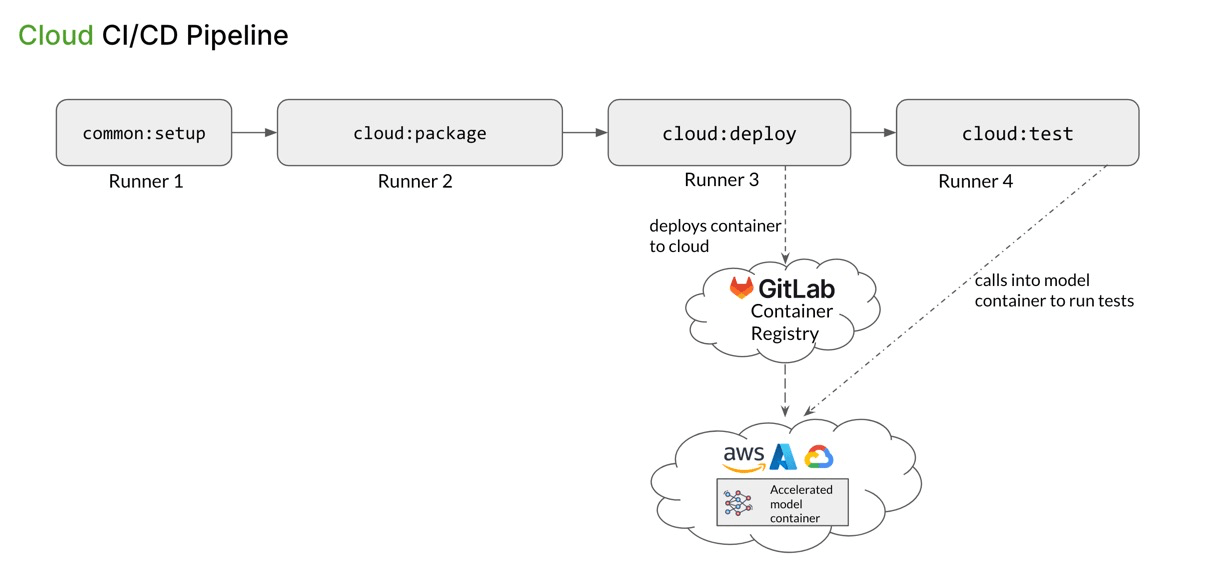
Each pipeline has four stages: setup, package, deploy, and test. Here’s the logical flow:
- common:setup - produces OctoML CLI binary artifact and passes it on to local:package
- cloud:package - packages the incoming model into a Docker tarball using the OctoML CLI binary and passes the tarball to the next stage
- cloud:deploy - builds a Docker image from the Tarball and deploys the docker container to a remote registry (in our example, we deploy it to AWS via GitLab Container Registry using Flux, but there can be other mechanisms)
- cloud:test - run the user-provided test script
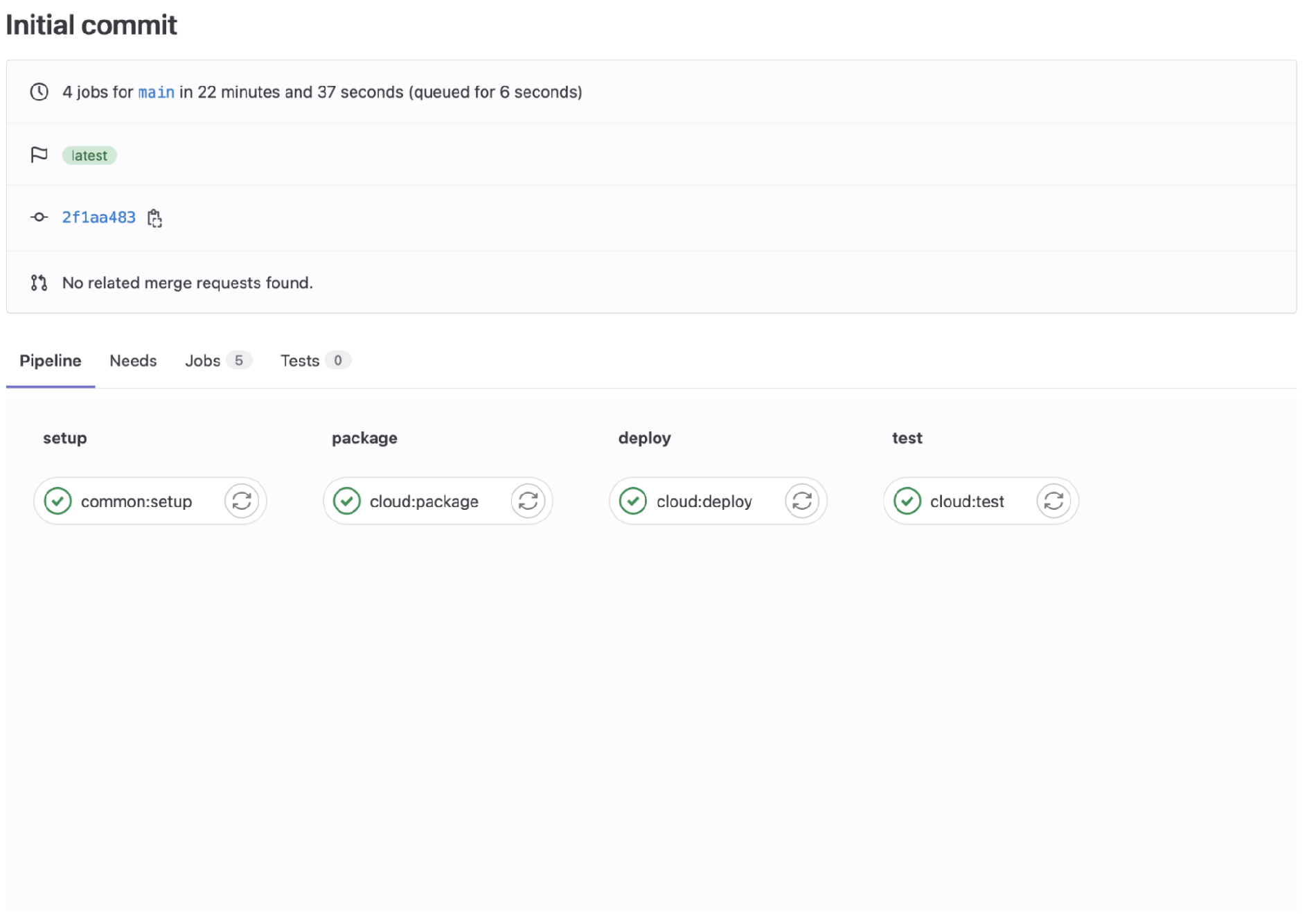
When a cloud pipeline is executed, the GitLab Pipeline UI will display a corresponding workflow:
Similar to any other GitLab CI/CD job, our example repository has YAML files that define how each stage will execute. You can easily clone the repository or code and adapt it to your custom model and inference code:
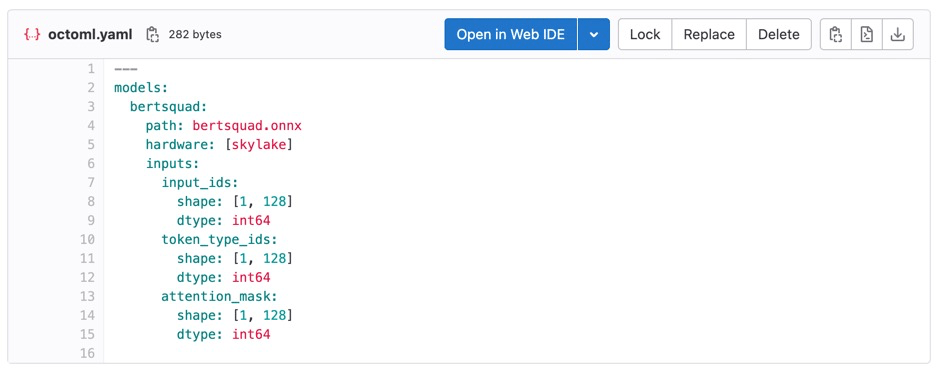
In addition to the stage YAML files, OctoML CLI also has its own octoml.yaml configuration, which defines the path to your model, hardware type the model should be accelerated for, and the model’s input shapes:
Get started with OctoML CLI and GitLab CI/CD
OctoML CLI and GitLab CI/CD unify your software engineering and machine learning pipelines by allowing ML models to be deployed using the same infrastructure and processes you’re currently using for software applications. Further, our integration makes it seamless to start with local model deployments to test end-to-end inference and move to accelerated cloud deployments with minimal changes to your workflow.
We’ve published tutorials with an NLP (Bertsquad) and Vision (YOLOv5) model for end-to-end examples. So, to get started, download the OctoML CLI and request an acceleration consultation to receive a token to OctoML’s SaaS platform.




