This blog is the latest post in an ongoing series about GitLab's journey to build and integrate AI/ML into our DevSecOps platform. The first blog post can be found here. Throughout the series, we'll feature blogs from our product, engineering, and UX teams to showcase how we're infusing AI/ML into GitLab.
Most development and engineering teams are now tasked with maintaining and deploying AI/ML-related code. In this context, the focus on security and efficiency becomes even more crucial. Companies are keen to capitalize on the benefits of AI swiftly while striving to decrease potential risks. GitLab can be used to orchestrate any AI/ML workloads, enabling teams to rapidly develop new generative AI capabilities. GitLab recently announced a partnership with Google to bring generative AI on Google Cloud to our mutual customers.
This is a tutorial of how to use these tools to deploy an AI model with Google Cloud's Vertex AI using GitLab to orchestrate the ModelOps workload. Our use case is a simple introductory credit card fraud detection model, a pertinent issue in the financial industry.
The solution
Our solution is a Python-based credit card transaction fraud detection app. Once deployed, applications can use an API endpoint to make predictions on whether a submitted transaction is fraudulent or not.
Vertex AI is Google Cloud's flagship AI/ML platform that lets users train and deploy machine learning models and AI applications. This is the platform where the API endpoint and model are hosted. While Vertex AI can handle training using prebuilt functions, this demo uses a custom training script written in Python.
For the demo’s purposes, GitLab hosts the application source code and helps to ensure quality and security by running the tests and scans automatically. We also use GitLab's CI/CD to execute the Python code, programmatically upload the resulting artifacts to Google Cloud Storage, and create the endpoint in Vertex AI.
Let's take a high-level look at how the solution is designed and what it does:
- Data preprocessing: To effectively detect fraudulent transactions, we address the initial imbalance in the raw transaction data. By employing the Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique (SMOTE), we duplicate instances of the minority class, enhancing the model's ability to identify patterns.
- Model training: Using the balanced dataset, we train a RandomForestClassifier model. This creates a 'forest' of decision trees, each based on a random subset of the training data. It outputs the mode of the classes determined by the individual trees, making it well-suited for binary outcomes, such as identifying fraudulent transactions. The trained model is stored in a Google Cloud Storage bucket for later use.
- Model deployment: Leveraging GitLab's DevSecOps platform, model deployment becomes straightforward. By committing the code to GitLab, the trained model is automatically deployed to Vertex AI. Subsequently, the API endpoint is also established.
Prerequisites
Before we dive into the details, let's make sure you have everything you need to get started with deploying your AI model using GitLab and Vertex AI.
Here are the requirements:
- Google Cloud project
- Google Cloud service account with these permissions:
- AI Platform Admin
- Service Account User
- Storage Admin
- Storage Object Admin
- Vertex AI Administrator
- GitLab project
Demo walkthrough
Following the video walkthrough, here's a guide for setting up an AI pipeline with GitLab and Google Cloud's Vertex AI.
Step 1: GitLab and Google Cloud connection
Firstly, we need GitLab to interact with Google Cloud. Insert your Google Cloud Service Account credentials into your GitLab project's environment variables (make sure they're Base64 encoded for security).
Step 2: Uploading data to Vertex AI
Move to the Vertex AI section in Google Cloud. Here, create and upload your dataset. In our demo, we use a 'Tabular' dataset for 'Classification' as we're predicting credit card fraud.
Step 3: Creating the CI/CD pipeline
Back to GitLab to structure our CI/CD pipeline. It comprises three stages:
Test: Quality and security checks.
Train: Executes a Python script to train the model, outputting a .pkl artifact.
train:
stage: train
script:
- apt-get update && apt-get install -y python3-pip
- pip3 install pandas scikit-learn joblib imbalanced-learn google-cloud-storage
- python3 src/train.py
artifacts:
paths:
- model.pkl
Deploy: Uses Google Cloud's Deep Learning platform container to deploy the trained model on Vertex AI.
deploy:
stage: deploy
image:
name: gcr.io/deeplearning-platform-release/sklearn-cpu
entrypoint: [""]
script:
- python src/deploy.py
dependencies:
- train
only:
- main
Step 4: Model training
The training code, running on GitLab CI/CD, fetches data from Vertex AI, processes it, trains our RandomForestClassifier model, and saves the model to Google Cloud Storage.
Step 5: Model deployment
The deployment script creates an endpoint on Vertex AI and deploys our trained model there, utilizing the service account credentials we set initially.
Step 6: Prediction testing
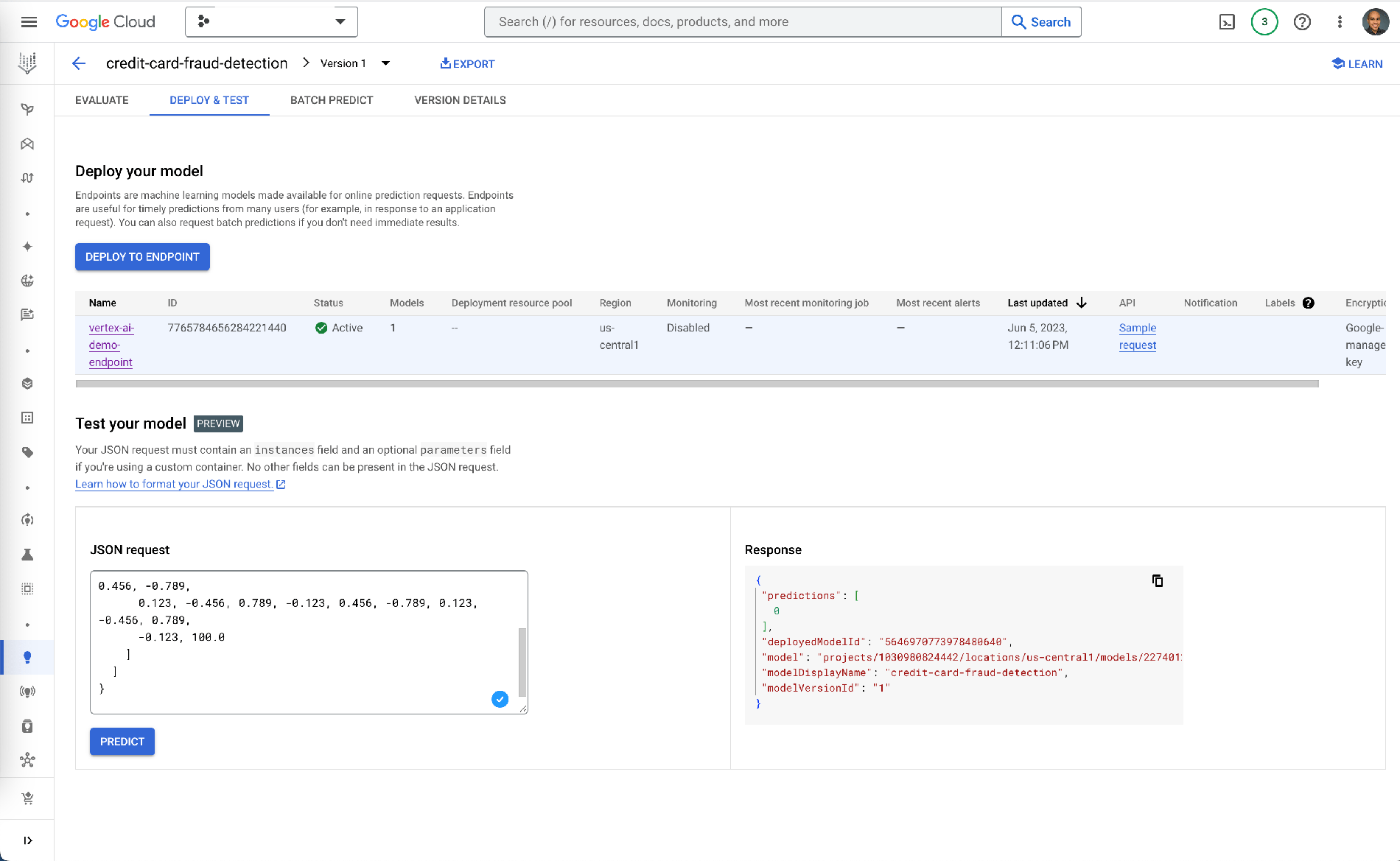
Finally, within Vertex AI, navigate to your model and test its predictions using an input JSON request. If all goes well, you'll get a response from your model.
There you have it: an AI pipeline with GitLab and Google Cloud's Vertex AI. This combination of GitLab's DevSecOps capabilities with Vertex AI's scalable ML platform is designed with the aim of rapid and secure AI deployments.




